Fixed: This Device Cannot Find Enough Free Resources... (Code 12)
Seeing "This device cannot find enough free resources that it can use... (code 12)" means a hardware conflict. We explain how to fix error code 12 through methods like disabling other devices, changing resource settings, and resolving IRQ conflicts to clear this error.
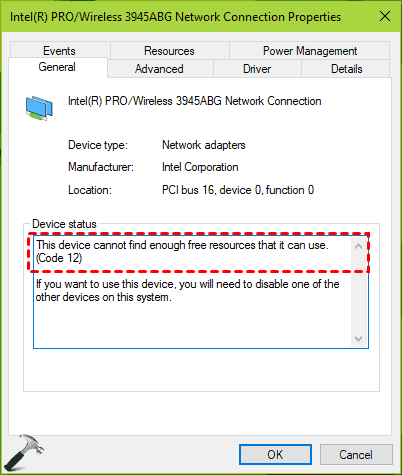
This Device Cannot Find Enough Free Resources That It Can Use Code 12 in Windows 10/11
Encountering the error message "This device cannot find enough free resources that it can use... (code 12)" in Device Manager is a frustrating experience. However, this error typically does not indicate an outdated or underpowered computer.
In most cases, it represents a fundamental communication failure within the system. Error code 12 signifies a resource allocation conflict, which occurs when two or more hardware components attempt to claim the same internal system pathways simultaneously.
About The Device Manager Code 12 Error
What does "This Device Cannot Find Enough Free Resources that it can use... (Code 12)" mean? Essentially, your computer operates using a framework of distinct addresses and dedicated communication channels for each internal hardware component. The error message "this device cannot find enough free resources that it can use... (code 12)" indicates that Windows has failed to allocate the necessary system pathways required for a device to function.
These "resources" are specific system elements:
- Input/Output (I/O) ranges.
- Interrupt Request (IRQ) lines.
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) channels.
They are essential, low-level conduits that enable communication between your CPU and all connected hardware.
The issue is their improper assignment. The system’s Plug and Play manager, responsible for coordinating these pathways, can become misconfigured. This may occur following the installation of a new device with overlapping requirements, a driver update that disrupts previous settings, or an incorrect BIOS/UEFI firmware configuration, particularly on laptops.
The outcome is consistently visible in Device Manager as a yellow alert icon next to the affected device, accompanied by the details for code 12.
Common Causes for Error Code 12 in Windows
There are some main reasons for that error code:
- A direct hardware conflict. This happens when two components, such as a Wi-Fi card and a sound card, are erroneously assigned the same IRQ channel. Since both cannot operate using the same channel, one is disabled, triggering the error.
- Faulty drivers. A driver acts as essential communication software between a hardware component and Windows. An outdated, corrupted, or incorrect driver can send improper instructions, leading the hardware to request invalid or inaccessible resources and generating the error.
- Outdated BIOS/UEFI settings. This firmware manages the initial hardware detection and configuration. Outdated firmware or disabled features like "Plug and Play OS" can incorrectly allocate resources before the operating system loads.
- Physical hardware failure. A malfunctioning device may report incorrect resource requirements, creating allocation conflicts that manifest as this error.
Having clarified these underlying reasons, we can now focus on effective resolution methods.
How to Fix Error Code 12 in Windows 10 and 11?
Now, we will show you the proven solutions. The goal is to reset the conversation between your hardware and Windows so they can divvy up the resources fairly.
Way 1. Restart Computer
The simplest trick is to restart your computer. A full reboot can force Windows to re-enumerate all hardware and re-assign resources from scratch, which might just clear the conflict temporarily or permanently.
Way 2. Reinstall Drivers
Besides, you can also try a driver reinstall if the restart is not working.
1. Go to Device Manager, right-click the problematic device, and select "Uninstall device".
2. Check the box that says "Delete the driver software for this device" if it appears.
3. Then, restart your computer.
4. Upon reboot, Windows will attempt to install a fresh, default driver, often with a clean slate for resource requests.
This might fix code 12 in Windows 10 or 11.
Way 3. Update Drivers to Resolve Code 12
If reinstalling drivers doesn’t work, the next move is to update the driver. Don’t just rely on Windows Update for this.
1. Visit the website of your computer’s manufacturer (Dell, HP, Lenovo) or the specific component maker (NVIDIA, Intel, Realtek).
2. Find the support or drivers section, enter your model number, and download the latest driver package specifically for your version of Windows.
3. Install it manually.
An updated driver often contains fixes for known conflicts and communicates more clearly with the system.
Way 4. Change Resources Settings in Device Manager
When the basic steps don’t make a dent, it’s time to roll up your sleeves. One powerful method is to let Windows try to resolve the conflict itself.
1. Right-click the Start button, and choose Device Manager.
2. In Device Manager, right-click the faulty device and choose "Properties".
3. Go to the "Resources" tab, and uncheck "Use automatic settings", click "Change Setting...".
4. Then see if you can manually assign a different configuration from the list.
Warning: this is advanced, and wrong settings can disable devices.
Way 5. Reset Resource Allocation in BIOS/UEFI
A more systemic approach is to reset resource allocation in your BIOS/UEFI.
1. Enter your BIOS setup (usually by pressing F2, Del, or F10 during startup).
2. Look for settings like "Reset to Defaults", "Load Optimized Defaults", or specific options for "Plug and Play OS" or "PCI Latency Timer".
3. Select the option and confirm when prompted.
4. Save and exit.
Loading optimized defaults can clear corrupted low-level settings. Also, ensure your BIOS is updated to the latest version from your manufacturer’s website, as updates frequently resolve hardware compatibility bugs.
Way 6. Disable Device in Device Manager
In some instances, the resource conflict involves a limited number of components. If the error affects a non-essential device—a legacy COM port, for example—you can attempt to disable that other device within Device Manager.
This action releases its allocated system resources, potentially making them available for the device you require. This process serves a dual purpose as both a diagnostic measure and a potential solution. If deactivating the first device successfully enables the second, you have identified the source of the conflict.
Troubleshooting "This Device Cannot Find Enough Free Resources" on a Touchpad
Integrated devices like touchpads are notorious for throwing this error, especially after system updates or hibernation.
The sudden appearance of "this device cannot find enough free resources that it can use code 12 touchpad" can be paralyzing on a laptop.
Try these ways:
- First, try the specific touchpad driver from your laptop maker's site—not the generic Microsoft precision driver.
- If that fails, check for conflicts with other human interface devices.
- Sometimes, a conflict with an external mouse driver or a disabled USB controller can trigger this.
- In rare cases, the conflict might be with the PS/2 port controller (the legacy port for keyboards/mice) in Device Manager, even if you’re not using it. Disabling that can sometimes free up the necessary IRQ for the modern touchpad to function.
FAQs About Code 12 Error
Q: What exactly are the "resources" in Code 12?
A: They're low-level system channels—IRQ (a device's "ring my bell" line to the CPU), I/O Range (its dedicated memory address), and DMA (a direct data pathway). When two devices fight over the same channel, Windows disables one with the Code 12 error.
Q: Does Code 12 on my GPU mean it's broken?
A: Not usually. It's typically a driver conflict. Use a tool like Display Driver Uninstaller (DDU) in Safe Mode to wipe the driver, then reinstall it fresh from NVIDIA/AMD. A conflict with another PCIe card is also common.
Q: Can a Windows update cause Code 12?
A: Yes. Major updates can disrupt resource allocation. The fix is usually to update the specific device driver to a version compatible with the new Windows build.
Q: Why does my touchpad get Code 12 after sleep?
A: This is a classic driver power management bug. The touchpad fails to reclaim its resources after wake-up. Update the touchpad driver from your laptop maker's site, or disable "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power" in its Device Manager properties.
Q: Is it safe to manually change resources in Device Manager?
A: Tread carefully. Manual assignment is advanced and can cause system instability. Exhaust all other fixes first and always note the original settings before changing anything.
Q: I've tried everything. What's the last resort?
A: If all software fixes fail:
- Isolate hardware: Remove non-essential expansion cards to find a conflict.
- System Restore/Repair Install: Roll back or perform an in-place Windows upgrade.
- Test for hardware failure: Try the device in another computer. If it fails there, too, the hardware itself is likely faulty.
Try Data Recovery Software If Needed
If you find that there are lost files on your computer due to some issues, you can try a powerful Windows data recovery software, like MyRecover. It provides the following benefits:
- Its primary advantage is its comprehensive scanning capability, which performs both a quick initial scan for recently deleted items and a thorough deep scan that meticulously examines the storage device sector by sector.
- The software is designed for read-only access during scanning, guaranteeing that the original data on your drive remains untouched and unaltered.
- It provides powerful filtering and preview functions. After a scan, users can sort results by file type and original path. You can also filter files by file size, name, and modified date. The integrated preview pane allows for visual confirmation of recoverable files.
- The software maintains broad compatibility, supporting recovery from a wide range of devices, including internal and external hard drives, USB flash drives, and SD cards. It is also compatible with multiple file systems like NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, and ReFS, making it a versatile tool for various data loss scenarios on the Windows platform.
Try it now if required!

- Recover Deleted Files Easily with Simple Clicks
- 1000+ File Formats Supported
- Support HDD, SSD, External Hard Drive, USB Drive, SD Card, etc.
- Quickly Find Files Using File Types, Name, Size, etc.
- Preview Files Before Recovering
- Recover Unlimited Data